In statistics stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations. Some of these clusters are selected randomly for sampling or a second stage or multiple stage sampling is carried out to form the target sample.
Stratified Sampling Research Methodology
Stratified Random Sampling Mathstopia
Stratified Sampling Msrblog
Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response efficiency.
Stratified sampling method. Example of Disproportional Sample. Well lets start with a single univariate histogram. Cluster random sampling is a sampling method in which the population is first divided into clusters A cluster is a heterogeneous subset of the population.
Each has a helpful diagrammatic representation. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. Since the data had been collected by stratified sampling the above method treating it as srs is the wrong way to compute the variance for this problem.
Stratified sampling It allows you draw more precise conclusions by ensuring that every subgroup is properly represented in the sample. Therefore stratified random sampling provides a higher degree of precision than simple random sampling Random Sampling Random sampling or probability sampling is a sampling method that allows for the randomization of sample selection. How the variance is computed depends on the method by which the sample was taken.
Stratified sampling is a type of sampling method in which the total population is divided into smaller groups or strata to complete the sampling process. In stratified sampling researchers divide subjects into subgroups called strata based on characteristics that they share eg race gender educational attainment etc. Cluster sampling refers to a sampling method wherein the members of the population are selected at random from naturally occurring groups called.
His desired sample size is only 1000. The strata is formed based on some common characteristics in the population data. All the same this method of research is not without its disadvantages.
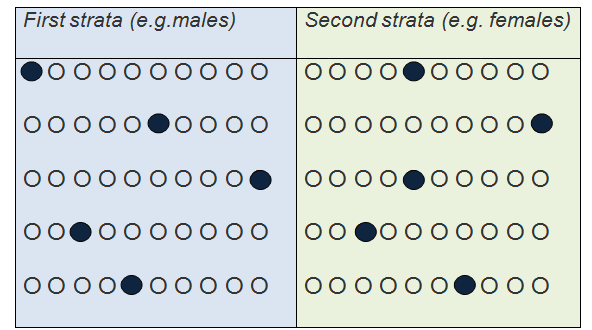
How does it work. Unlike the simple random sample and the systematic random sample sometimes we are interested in particular strata meaning groups within the population eg males vs. In stratified random sampling.
After dividing the population into strata the researcher randomly selects the sample proportionally. Since the 1000 subjects needed for the survey is 10 of the entire population sampling proportion suggests that 810 be female and 210 be male. In statistical surveys when subpopulations within an overall population vary it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation stratum independently.
Of stratified sampling where the weights are provided in terms of strata sizes. Respect to the characteristic under study then the method of simple random sampling will yield a homogeneous sample and in turn the sample mean will serve as a good estimator of the population. Gender age range income bracket job role.
In stratified sampling the population is partitioned into non-overlapping groups called strata and a sample is selected by some design within each stratum. We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias. A random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason.
To use this sampling method you divide the population into subgroups called strata based on the relevant characteristic eg. For example geographical regions can be stratified into similar regions by means of some known variables such. In disproportionate stratified random sampling the different strata do not have the same sampling fractions as each other.
Suppose for example a researcher desires to conduct a survey of all the students in a given university with 10000 students 8000 females and 2000 males. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias and common examples include. This video describes five common methods of sampling in data collection.
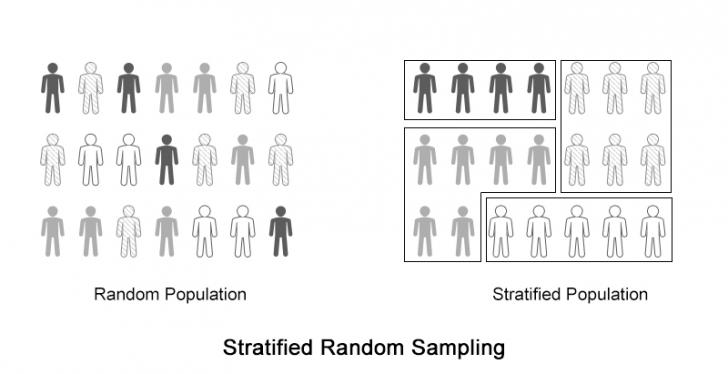
The population is first divided into homogeneous subpopulations or stratas that are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. This sampling method is also called random quota sampling. A probability sampling method is any method of sampling that utilizes some form of random selectionIn order to have a random selection method you must set up some process or procedure that assures that the different units in your population.
Ad_1 Stratified random sampling benefits researchers by enabling them to obtain a sample population that best represents the entire population being studied. Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves dividing a population into smaller groupscalled strataThe groups or strata are organized based on the shared characteristics or. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique see our article Probability sampling if you do not know what probability sampling is.
Stratified sampling enables use of different statistical methods for each stratum which helps in improving the efficiency and accuracy of the estimation. We did the computation just to show that if hypothetically. Stratified sampling is a method created in order to build a sample from a population record by record keeping the original multivariate histogram as faithfully as possible.
Stratified sampling is one in which the population is divided into homogeneous segments and then the sample is randomly taken from the segments. Stratified Sampling Cluster Sampling. 000 Introduction015 Definition of.
Nonprobability sampling is any sampling method where some elements of the population have no chance of selection these are sometimes referred to as out of coverageundercovered or where the probability of selection cant be accurately determined. Stratified Random Sampling is a probability sampling method found in market research software that uses a two-step process to select the sample group. For instance if your four strata contain 200 400 600 and 800 people you may choose to have different sampling fractions for each stratum.
It involves the selection of elements based on assumptions regarding the population of interest which forms the criteria for selection. Cluster Sampling is a method where the target population is divided into multiple clusters. Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller sub-groups known as strata.
Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling using which researchers can divide the entire population into numerous non-overlapping homogeneous strata. Random sampling examples include. Cluster Sampling and Stratified Sampling are probability sampling techniques with different approaches to create and analyze samples.
Simple systematic stratified and cluster sampling. Once divided each subgroup is randomly sampled using another probability sampling method. An Overview Stratified random sampling involves first dividing a population into subpopulations and then applying random sampling.
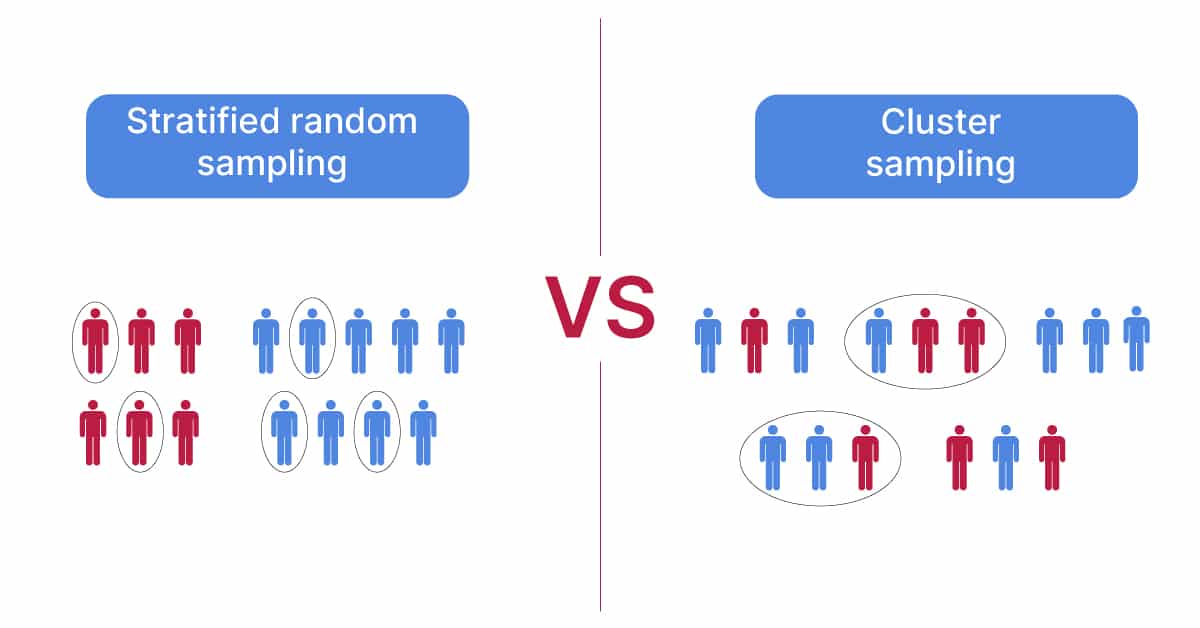
Stratified Sampling Vs Cluster Sampling Voxco

Cluster Sampling Vs Stratified Sampling What S The Difference
1

Section 4 Stratified Random Sampling

7 A Under What Circumstances Is Stratified Random Sampling Procedure Is Considered Appropriate How Would You Select Such Samples Explain By Means Of Ppt Video Online Download
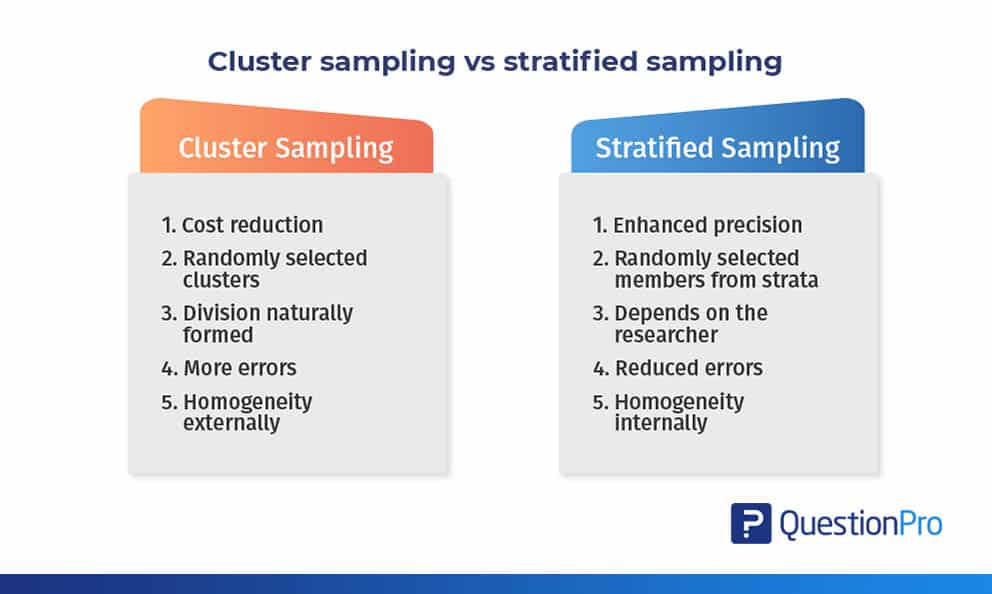
Cluster Sampling Vs Stratified Sampling Questionpro
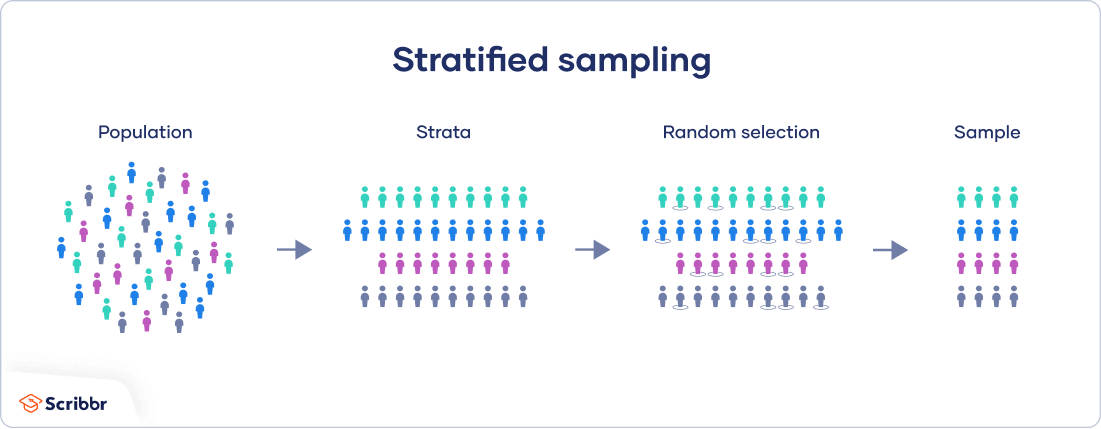
Stratified Sampling A Step By Step Guide With Examples

Stratified Sampling Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
