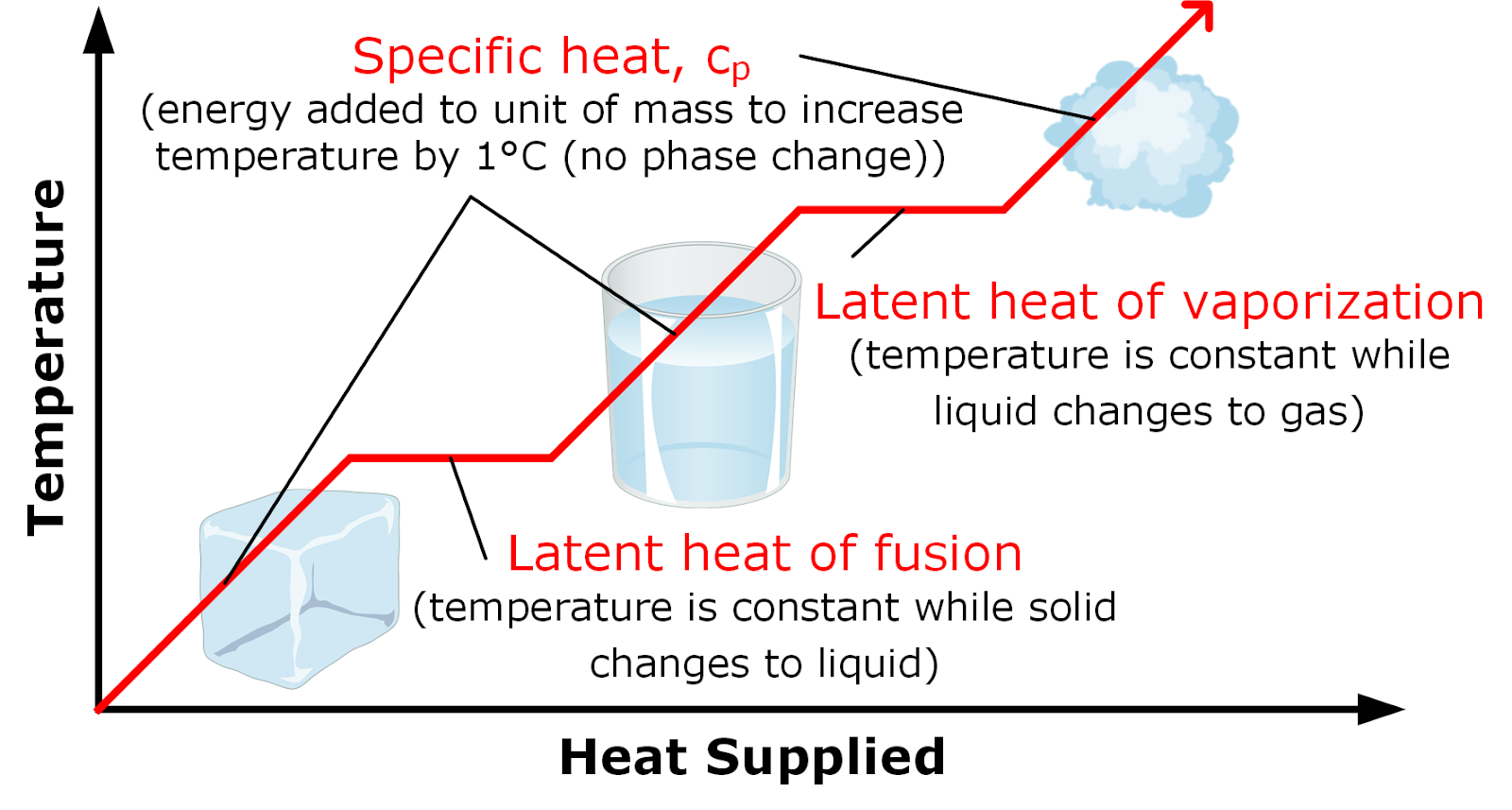
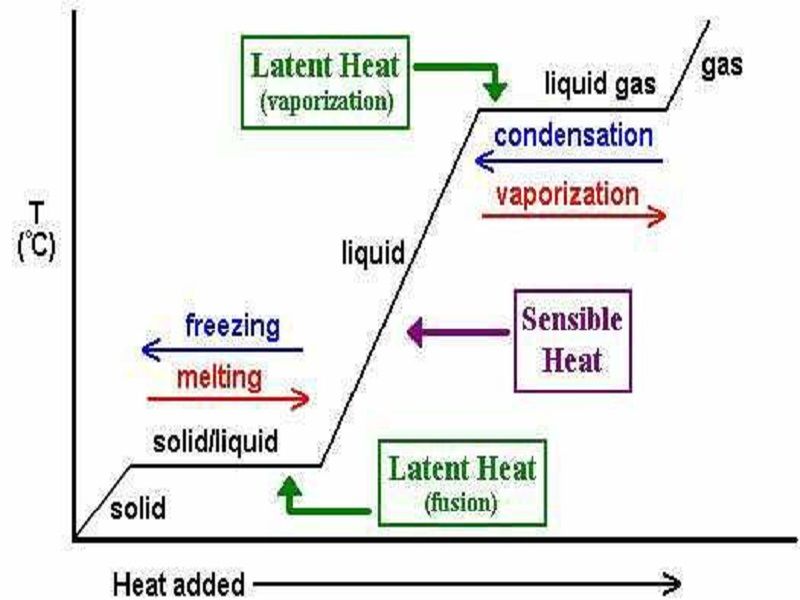
Latent heat of vaporization. When latent heat is added no temperature change occurs.
General Physics Ii
Specific Latent Heat Of Vaporization Tec Science
What Is Steam Industrial Controls
The specific heat at constant pressure is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of a.

Latent heat of vaporization. The latent heat of vaporization differs for various liquids. The latent heat of vaporization H vap also known as the enthalpy of vaporization or evaporation is the amount of energy enthalpy that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a given quantity of the substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place.
For this energy is needed and this energy is known as the latent heat of vaporization. The term latent heat of vaporization is the amount of heat required for the transformation of a liquid at its boiling point to gas at a constant temperature. Latent heat is the work done in a system in order to hold the atoms or molecules of matter in the same phase.
This is a solid turning into a liquid. The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of.
So in effect the. The heat of vaporization is a latent heat. Although sensible heat is often called latent heat it isnt a constant-temperature situation nor is a phase change involved.
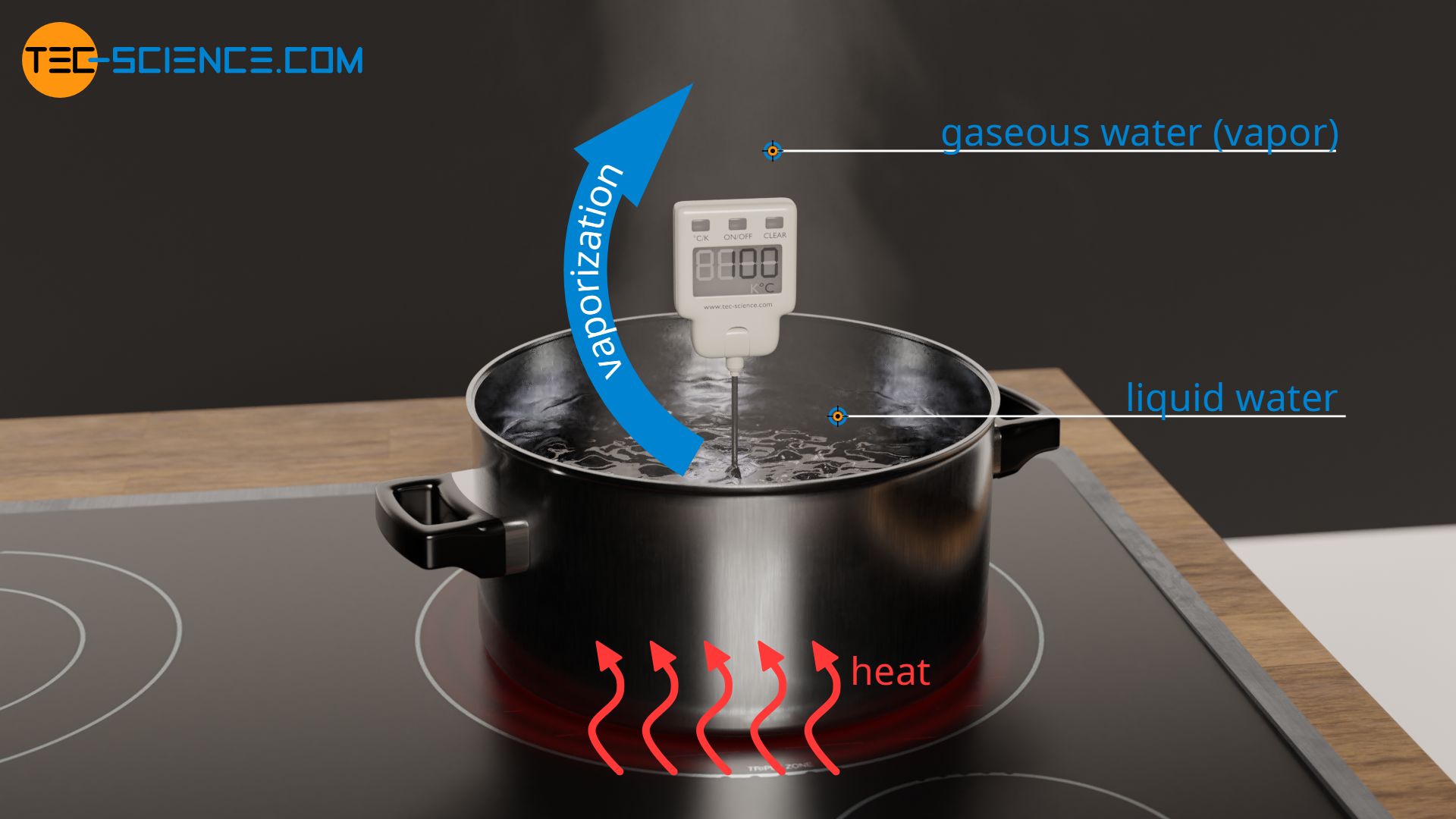
Water has a high latent heat of vaporization which is why steam burns are so dangerous. A substance condensing or vaporizing at a specified temperature and pressure. The latent heat of vaporization is the heat absorbed or released when matter vaporizes changing phase from liquid to gas phase at a constant temperature.
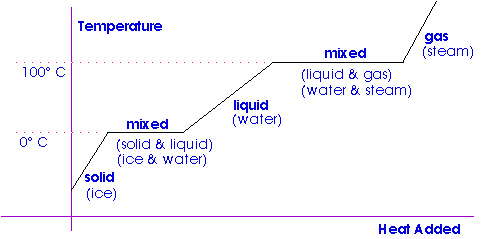
Vaporization is the process of conversion of matter from the liquid state into the vapour state. Specific heat capacity and heat of vaporization of water. For example when a pot of water is kept boiling the temperature remains at 100 C until the last drop evaporates because all the heat being added to the liquid is absorbed as latent heat of vaporization and carried away by the.
However when this phase change occurs at this temperature heat energy is absorbed by water molecules to break the bonds but it will not increase the temperature more. L latent heat of vaporization 245 MJ kg-1 c p specific heat at constant pressure 1013 10-3 MJ kg-1 C-1 e ratio molecular weight of water vapourdry air 0622. The latent heat of vaporization is also referred to as the enthalpy of vaporization.
Latent heat is the additional heat required to change the state of a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point or from liquid to gas at its boiling point after the temperature of the substance has reached either of these points. That associated with vaporizing a liquid or a solid or condensing a vapour is called the heat of vaporization. Its units are usually Joules per gram Jg or calories per gram calg.
The latent heat of fusion of ice is 334 x 10⁵ joules per kilograms or 334 x 10⁵JKg. For water this phase change occurs at 100C boiling point of water. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
The diagram on the left shows the uptake of heat by 1 kg of water as it passes from ice at -50 ºC to steam at temperatures above 100 ºC affects the temperature of the sample. Latent heat is the extra heat required to change the condition of a substance from solid to fluid at its softening point or from fluid to gas at its breaking point after the temperature of the substance has come to both of these focuses. Latent Heat of Vaporization.
Latent Heat of Vaporization. Latent heat is the heat absorbed or released as the result of a phase change. This process leaves temperature unaffected - it wont get higher or lower.
Heat necessary to transform 1 kg of ebullient water into vapour without change of temperature thermal energy necessary during the change of state liquid to the state vapour. Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a change in phase. Latent heat is defined for a system with constant temperature.
The enthalpy of vaporization symbol H vap also known as the latent heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation is the amount of energy that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gasThe enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place. The latent heat we cant use the latent heat of vaporization. Structure of water and hydrogen bonding.
Latent heat can be understood as energy in hidden form which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature. Heat of fusion is the amount of heat energy required to change the state of matter of a substance from a solid to a liquidIts also known as enthalpy of fusion. Water boils and absorbs latent heat of vaporization.
Here is the Latent Heat table which shows the latent heat of vaporization and change of phase temperatures for some of the common fluids and gases. Examples are latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization involved in phase changes ie. Therefore this term describes the change of phase regarding the internal energy of the system.
Both L f and L v depend on the substance particularly on the strength of its molecular forces as noted earlier. Latent heat is an intensive property measured in units of Jkg. Specific heat of steam.
Latent comes from the Latin latere which means to lie hidden or concealed. L f and L v are collectively called latent heat coefficients. Latent originates from the Latin word latere which intends to lie covered up or hid.
V latent heat of vaporization liquid-gas 25 106Jkg 1 at 0 C l f latent heat of fusion solid-liquid 334 105Jkg 1 at 0 C l s latent heat of sublimation solid-vapor 283 106Jkg 1 at 0 C l s l f l v However the latent heat is a property of the system and depends on the ther-modynamic state generally expressed as a function of. Thats latent heat of fusion that we need and the latent heat of fusion for water is about 333000 joules per kilogram which gives you 999000 joules of heat in order to turn this ice at zero degree Celsius into water at zero degrees Celsius. Steam absorbs heat and thus increases its temperature.
Capillary action and why we see a meniscus. Latent Heat Flow - Latent heat is the heat when supplied to or removed from air results in a change in moisture content - the temperature of the air is not changed. In contrast to sensible heat latent heat is the energy released or absorbed that changes the state of a body during a constant temperature process.
The heat of vaporization is latent heat. They are latent or hidden because in phase changes energy enters or leaves a system without causing a temperature change in the system. The most common forms of latent heat are fusion and vaporization.
Latent heat energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state phase that occurs without changing its temperatureThe latent heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid is called the heat of fusion. As more heat is added the vaporization process continues with a corresponding increase in the volume. Hydrogen bonds in water.
The latent heat is normally expressed as the amount of heat in units of joules or calories per mole or unit mass of the substance undergoing a change of state. Rise in temperature as liquid water absorbs heat. This energy breaks down the intermolecular attractive forces and also must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas the pΔV work.
When steam burns a persons arm for example this energy transfer causes the steam to condensewhich uses much more energy than simply changing the temperature. Hydrogen bonding in water. Melting and Boiling Temperatures - Evaporation and Melting Heats of common Materials - Melting and boiling point temperatures latent heat of evaporation and melting heat of common substances like copper gold lead and more - SI.
States Of Matter Fd202 Fundamentals Of Fire And Combustion On Guides
Heat Of Vaporization Of Ethanol From Dortmund Data Bank

Buy Latent Heat Of Vaporization Of Ammonia Classic Reprint Book Online At Low Prices In India Latent Heat Of Vaporization Of Ammonia Classic Reprint Reviews Ratings Amazon In
What Is The Latent Heat Of Vaporisation Quora
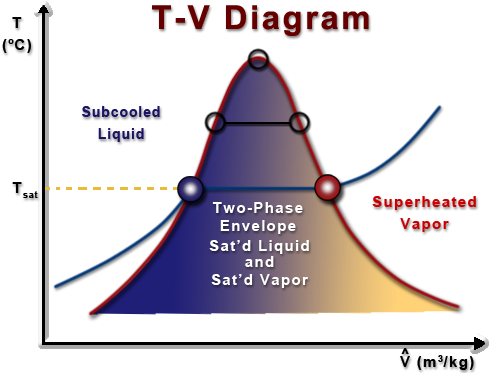
Ch3 Lesson E Page 3 Is The Heat Of Vaporization Constant
9 Latent Heat Examples In Daily Life Studiousguy

Latent Heat Of Fusion And Vaporization Specific Heat Capacity Calorimetry Physics Youtube

Latent Heat Of Vaporization And Fusion Definition Teachoo